
As wildfires increasingly threaten ecosystems, communities, and economies across the United States, understanding and managing these risks has become imperative. Verisk has compiled a comprehensive set of state-specific wildfire data to address these challenges, focusing on risk assessment, historical context, and current trends. Verisk’s Wildfire Risk Report is designed to empower insurers, policymakers, community leaders, and underwriters with insights that can inform risk management strategies and promote resilience in vulnerable areas.
Wildfires are not just a seasonal concern; they represent a growing existential threat exacerbated by climate change, urban expansion, and land management practices. Each year, billions of dollars in damage are incurred, and lives are disrupted as wildfires consume vast landscapes. In this context, the importance of robust data and analysis cannot be overstated. The Wildfire Risk Report serves as an essential resource for stakeholders looking to develop effective response strategies, improve insurance coverage, and enhance community preparedness against the backdrop of rising wildfire activity.
This compilation provides an exhaustive analysis of wildfire risks, including a detailed risk assessment that categorizes structures into negligible, low, moderate, and high to extreme levels, thereby identifying the most vulnerable areas. It also explores significant historical wildfire events, detailing acreage burned, and the financial repercussions faced by affected communities and insurers. Additionally, it highlights high-risk counties and the prevalence of structures within wildland-urban interface (WUI) areas, examining how construction and mitigation efforts impact these vulnerabilities. Through these comprehensive reports, stakeholders—including underwriters—can gain a nuanced understanding of wildfire risks and make informed decisions to mitigate potential impacts
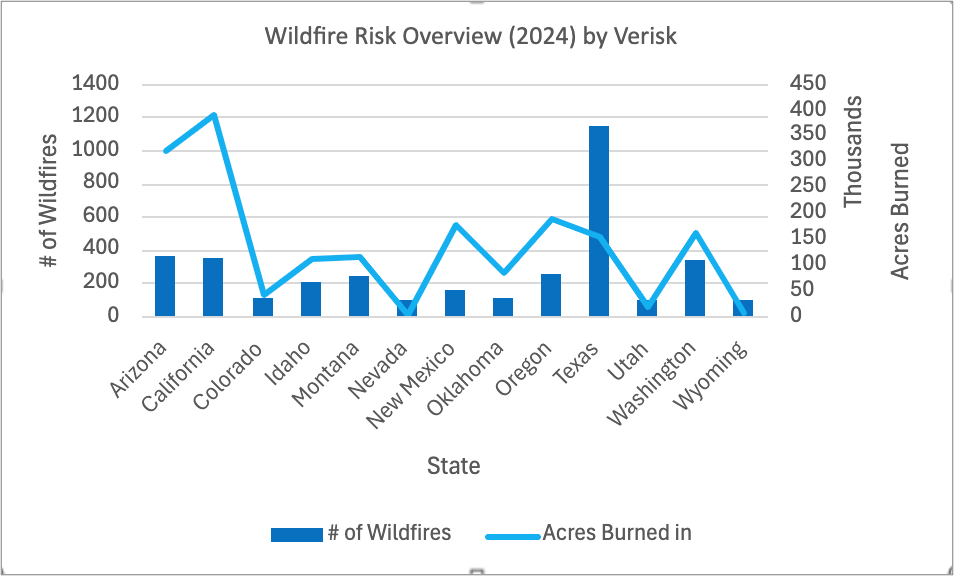
Wildfire Risk Overview
The data highlights significant variations in wildfire activity across states. Texas and California experience the highest numbers of wildfires, with California leading in total acreage burned. Conversely, states like Nevada, with fewer acres burned, have a high burn-per-fire ratio, indicating intense but smaller fire occurrences. The average wildfire count across states is 272 fires, impacting around 136,754 acres each. States like Wyoming and Nevada show a trend where fewer wildfires result in a larger proportion of acreage burned, contrasting with larger states where fire distribution is broader across acreage.
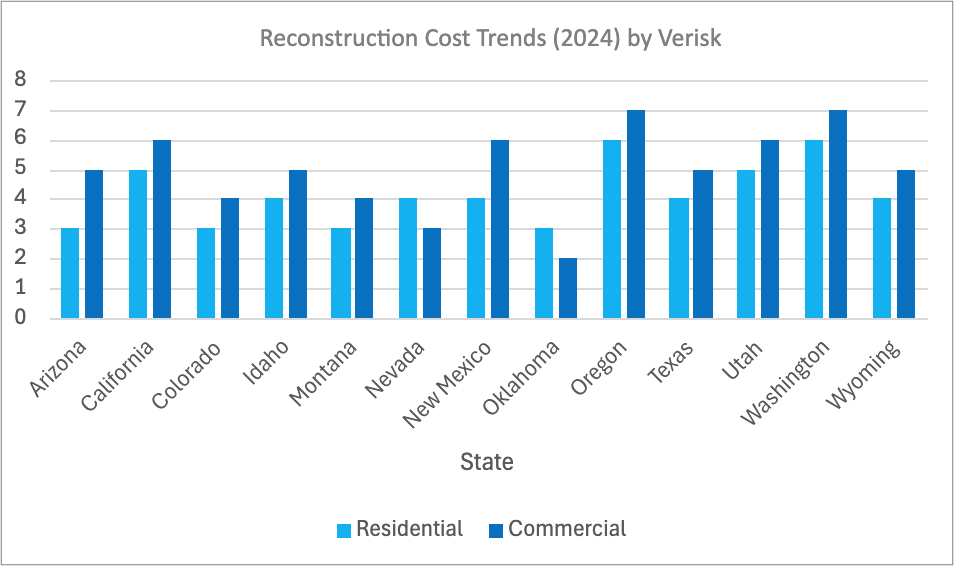
Reconstruction Cost Trends (2024)
Commercial reconstruction costs generally exceed residential, with Washington and Oregon incurring the highest costs for both. California and New Mexico also show relatively high costs in both categories, reflecting possible regional economic and structural factors affecting rebuilding expenses. This trend highlights potentially higher expenses in urbanized or commercially concentrated areas.
The data compiled in this report underscores the urgent need for enhanced risk management and mitigation strategies in wildfire-prone areas. Significant financial and risk exposure across multiple states reveals potential losses reaching billions of dollars, emphasizing the necessity for insurers, policymakers, and community leaders to collaboratively develop effective strategies for managing these escalating wildfire risks. The findings highlight the importance of comprehensive understanding and preparedness, especially as historical trends and current climate challenges reveal the increasing threat of wildfires.
Key insights from the report demonstrate the substantial financial implications of high wildfire risks, which necessitate a robust approach to insurance coverage and community readiness. Historical data on past wildfire events, coupled with current trends, underscores the growing challenges faced due to climate change and land use practices. Moreover, active mitigation efforts are critical for reducing risks, and community engagement in these initiatives can significantly enhance safety and resilience. As reconstruction costs rise, updated property data will be vital for accurate risk assessment and coverage adjustments.
To effectively address these challenges, stakeholders are encouraged to enhance risk models, invest in local and state-level mitigation programs, and update insurance coverage plans to align with current data. As wildfires continue to escalate in frequency and intensity, a proactive approach to risk management, alongside community engagement, will be essential for safeguarding lives and property. The insights gleaned from this report serve as invaluable tools for navigating the complexities of wildfire risks and fostering a culture of resilience in at-risk communities.




















 Execs, Risk Experts on Edge: Geopolitical Risks Top ‘Turbulent’ Outlook
Execs, Risk Experts on Edge: Geopolitical Risks Top ‘Turbulent’ Outlook  Insurance Groundhogs Warming Up to Market Changes
Insurance Groundhogs Warming Up to Market Changes  Modern Underwriting Technology: Decisive Steps to Successful Implementation
Modern Underwriting Technology: Decisive Steps to Successful Implementation  20,000 AI Users at Travelers Prep for Innovation 2.0; Claims Call Centers Cut
20,000 AI Users at Travelers Prep for Innovation 2.0; Claims Call Centers Cut 




